A carbohydrate-free diet is an extreme version of a low-carbohydrate diet in which the diet focuses on protein, healthy fats, and fiber.
Our body usually uses carbohydrates (glucose) to supply energy to the body and brain. Reducing them leads to a decrease in the production of insulin in the body, as a result of which it begins to break down protein (muscle stores) and stored fats as an alternative source. This leads to rapid weight loss.
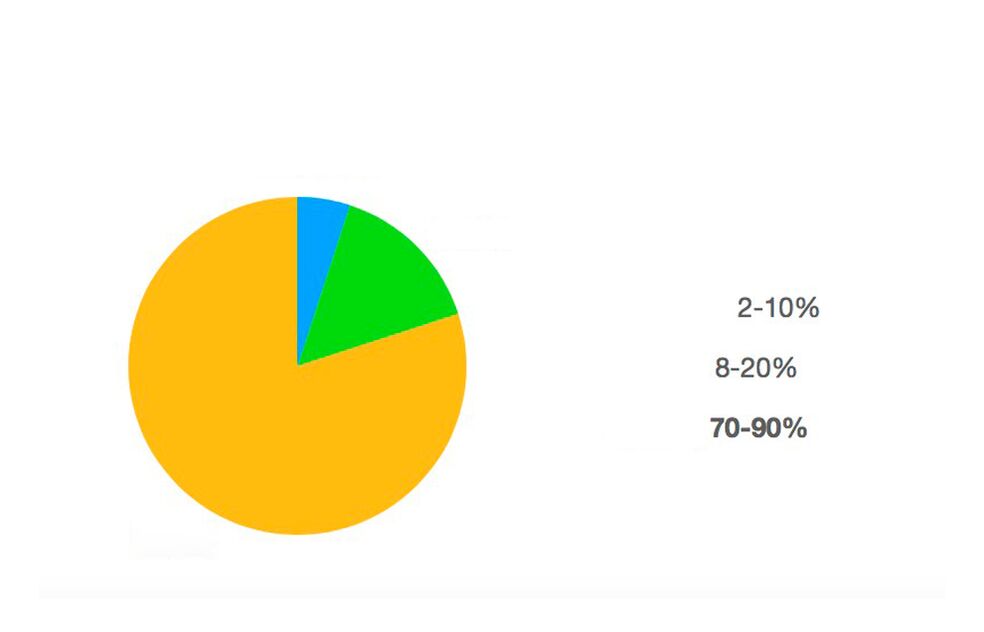
Depending on age, weight, physical activity and goals (weight loss, muscle gain, body dryness), the body requires different amounts of protein, fat and carbohydrates (BJU). According to experts, the average daily consumption is as follows:
- 45-65% carbohydrate
- 20-35% fat
- 10-35% protein
With a low carb diet, fats become the main source of calories and carbs are reduced to 2-10%.
The general principles of a carbohydrate-free diet are:
- The amount of carbohydrates consumed is reduced from 0 grams per day to 30 grams.
- Make sure you drink at least 8-12 glasses of water a day to get toxins out of your body.
- Since most of your diet consists of proteins and fats, you need to focus on the benefits. It is important to reduce the consumption of trans fats and not overuse saturated fats. For example, a 2018 study argues that a low-carbohydrate diet that favored plant-derived proteins and fats over animal sources has lower mortality. Think not only about lowering your waist, but also about your long-term health.
- It is almost impossible to completely avoid carbohydrates as they are found in many foods. But above all, those with a glycemic index above 50 should be avoided.
The most popular type of low carb diet today is the keto diet, which has a BJU ratio of 75% fat, 20% protein and 5% carbs. In addition, one of the most famous and popular is the Ducan diet, which is the basis of the diet in which proteins are present.
Advantages and disadvantages of a carbohydrate diet
Any diet is limited and stressful, so it’s important to assess all the pros and cons of a future diet before experimenting with nutrition.
Benefits of a carbohydrate-free diet
- Replacing carbohydrates with protein affects the hunger hormone ghrelin, which causes a feeling of fullness and can reduce snacks and daily caloric intake.
- Weight loss will be rapid in the first few weeks. This is mainly due to a decrease in fluid intake. Foods rich in carbohydrates not only contain a lot of water, but are also excreted through metabolism. This is why a carbohydrate-free diet is often chosen by those who want to lose weight fast. A study of 79 obese adults found that at 6 months, those who restricted their carbohydrate intake to less than 30 grams per day lost about 4 kg more than those who instead limited their fat intake.
- Carbohydrate intake significantly affects blood sugar levels and insulin levels. Excess glucose is linked to a number of health problems, such as type 2 diabetes, cancer, and cardiovascular disease. A low carb diet reduces the likelihood of these occurring.
- Research shows that a carb-free diet can reduce the symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease and slow its progression.
Disadvantages of a carbohydrate-free diet
- By reducing the amount of carbohydrates consumed, insulin levels decrease and the hormone glucagon increases, causing the body to burn fat. However, when the body becomes this form of fat burning, a process called ketosis occurs and compounds called ketones accumulate in the body. This process can cause side effects such as nausea, headache, halitosis, fever, sleep disturbances, and so on. In addition, fatigue and drowsiness are common. As a result, problems arise in everyday life, including a significant reduction in the number of workouts and a deterioration in the quality of their performance.
- A low carb diet will inevitably lead to fiber deficiency. Plenty of research suggests that the effects of beneficial bacteria in the gut when consuming dietary fiber are essential to overall health. Bacteria work on the grid to form short-chain fatty acids that prevent the growth of harmful bacteria, preserve intestinal health, and have anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects. In addition, it is difficult for such a diet to provide the body with sufficient amounts of vitamins, especially groups B and C, as well as minerals such as potassium.
- Long-term adherence to a diet can increase the risk of high cholesterol, osteoporosis, abnormal heart rhythm, and kidney problems.
- The most common side effects of a carbohydrate-free diet are constipation or indigestion.
Who is not suitable for a low carb diet?
- People with diabetes or chronic illness who need close blood sugar control.
- Problems with the cardiovascular system, blood pressure and gastrointestinal tract.
- Pregnant and lactating women.
- Elderly people, adolescents and those with low body mass index.
- People with emotional or psychological problems with food, including eating disorders.
Before trying a carb-free diet, consult a professional to make sure it doesn’t hurt.
General rules for a carbohydrate-free diet
Low carb foods contain mainly oils: coconut, butter or ghee, olive (virgin), avocado oil, etc.
Although all oils and fats are 0 or minimal carbs, not all are healthy. Some oils are processed and contain chemicals. In addition, most vegetable oils contain a lot of omega-6 fatty acids, which can cause inflammation if consumed in excess. These fats may also inhibit the anti-inflammatory activity of other fats, such as omega-3s.
For this reason, it is best to avoid omega-6 fatty acid-rich oils such as soybeans, corn, canola and peanut butter.
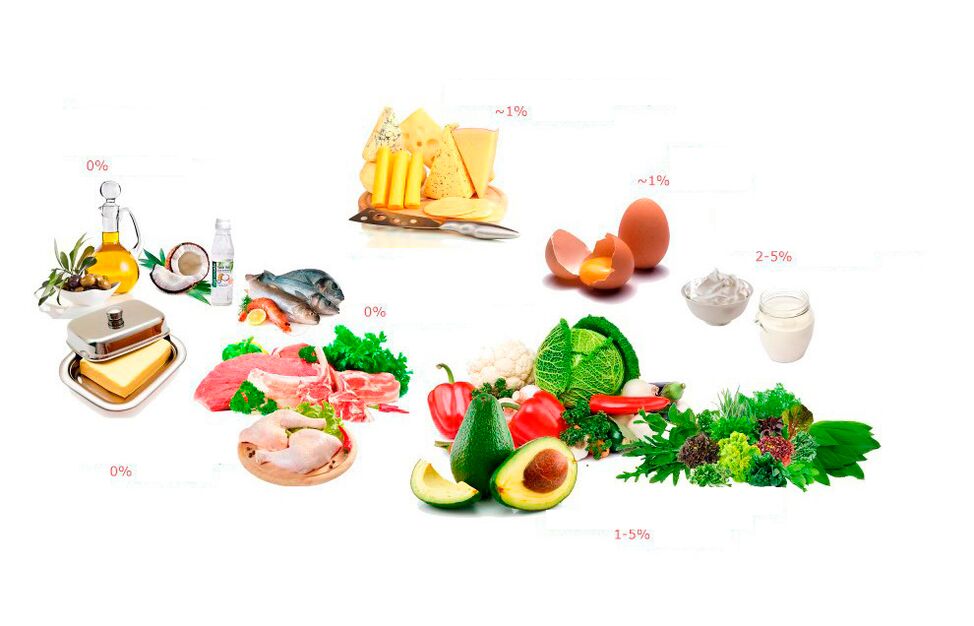

Since the diet will mostly consist of meat, which consists mainly of proteins and fats, make sure it is high quality and ideally organic, with no additives, as its main purpose is to improve the taste and prolong the shelf life of the product. Do not buy processed meat products. Many manufacturers add sugar, spices and flavors to increase the amount of carbohydrates.
Although dairy products contain carbohydrates (sugar in the form of lactose), they are mostly negligible. Sour milk can be used to get protein, calcium, vitamin D and potassium. Milk and yogurt are most carbohydrates, but if you’re not ready to completely cut them out, choose products without added sweeteners or flavors, and it’s important to pay attention to the number of servings.
Particular attention should be paid to food processing. During the diet, use recipes that include boiling, steaming, steaming. Baking is useful. And you better reject fried foods altogether.
In addition, you should choose foods with a low glycemic index (up to 50). They are full of slow carbohydrates that take a long time to break down and create a feeling of fullness. In general, it is worth remembering that they do not gain weight from carbohydrates, but from an excessively high-calorie diet and a sedentary lifestyle.
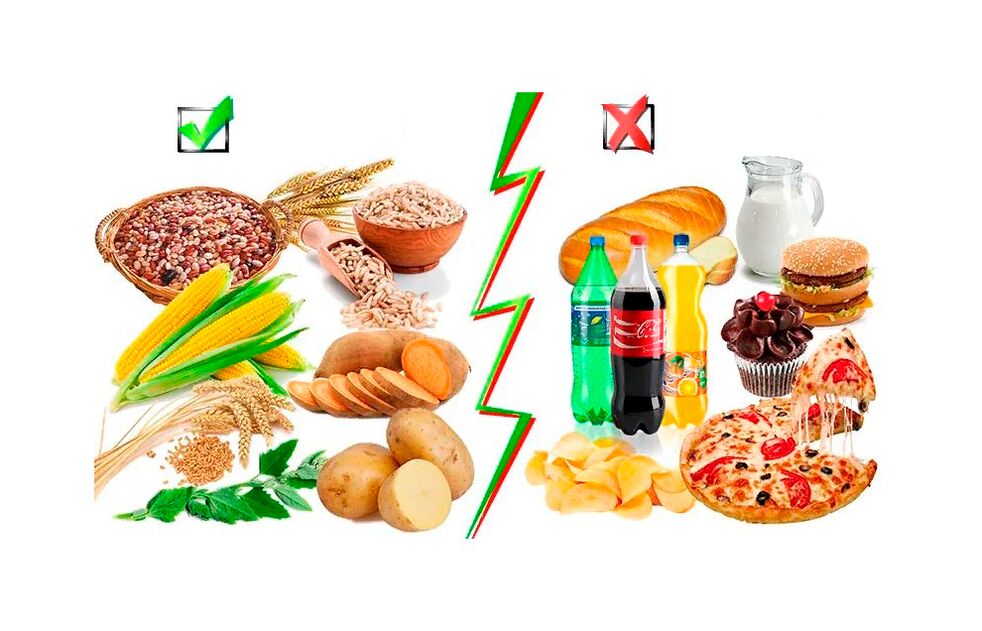

What foods should I eat and avoid on a carb-free diet?
Healthy foods are low in carbohydrates
- Meat and low-carbohydrate animal products: chicken, beef, turkey, lamb, pork, eggs, butter, cheese
- Seafood: salmon, catfish, cod, crab, sardines, herring, anchovies, trout
- Spices: herbs and spices
- Low calorie drinks: water, black coffee and tea
- Nuts and seeds (low carb): almonds, walnuts, pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds, pistachios, cashews
- Non-starchy vegetables and fruits, rich in fats: broccoli, zucchini, peppers, eggplant, cucumbers, cauliflower, leafy greens, brussels sprouts, celery, asparagus, mushrooms, coconut, avocado
Foods to avoid
A carbohydrate-free diet severely restricts and excludes many food groups, including:
- Cereals and cereals: rice, barley, quinoa, wheat, bread, pasta
- Sweets and cakes: cakes, pastries, candies
- Carbonated and sugary drinks
- Fruits and berries: apples, oranges, bananas, kiwis, pears
- Starchy vegetables: peas, corn, zucchini, potatoes
- Legumes: beans, chickpeas, lentils, peas
- Dairy products: milk and yogurt
- Spices with added sugar: ketchup, barbecue sauce, salad dressings
- Alcohol: beer, wine, liqueur, sweet cocktails, port wine, vermouth
Carbohydrate-free menu for a week
Although the list of available foods is significantly reduced, the diet can be varied. Example of a daily carb-free diet menu.
Monday
Breakfast: omelette with mushrooms
Lunch: beef soup
Dinner: oven-baked turkey fillet with asparagus
Tuesday
Breakfast: flaxseed bread, guacamole and poached egg
Lunch: miso soup
Dinner: baked zucchini with cheese
Wednesday
Breakfast: salad with salmon and avocado
Lunch: broth with chicken dumplings
Dinner: pasta with bacon and cream sauce
Thursday
Breakfast: salad with chicken, cucumber, feta and spinach
Lunch: zucchini pasta with stewed chicken slices
Dinner: peppers stuffed with seafood
Friday
Breakfast: casserole with cottage cheese
Lunch: mushroom soup
Dinner: steak and vegetables
Saturday
Breakfast: eggs with bacon
Lunch: brown rice with trout
Dinner: braised cabbage with meat
Sunday
Breakfast: oatmeal with a few almonds and boiled eggs
Lunch: boiled chicken with green peas
Dinner: seafood and vegetable salad

Keep in mind that a total and long-term ban on carbohydrate intake is extreme, and extreme eating habits are not good. A proper diet should be balanced and contain all the vitamins and nutrients needed for the body to function effectively. Experts have expressed mixed opinions on low-carbohydrate and low-carbohydrate diets, but they all agree that such a diet should be short-term and should be followed for up to 2 months.















































































